Human skin senses
In humans, pain (including itch), cold, warm and touch (including light pressure, deep pressure, vibration and tickle) are perceived by different nerve endings. Skin, the largest and most exposed organ of human body, is endowed with numerous sensory nerve endings.Ruffini endings
- Ruffini corpuscle is a slowly adapting mechanoreceptor existing in the human subcutaneous tissues.
- This receptor is spindle shaped and perceives the stimulus of stretch and touch.
- It monitors the slippage along the skin and helps the mechanism of gripping a object.

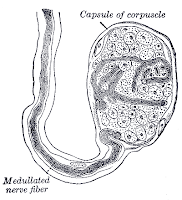
Meissner's corpuscles
- Meissner's corpuscles are rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors having highest sensitivity and they convey the senses of light touch.
- Though they are distributed throughout the human skin, they are more concentrated in fingertips, lips, tongue, soles and palms in human body.
- They are located primarily just below the epidermis and convey the feeling of touch.
.jpg)
Pacinian corpuscles
- Pacinian corpuscles are mechanoreceptors in the human skin responsible for pain and pressure senses.
- This receptors are larger and are fewer in number. The corpuscle about one mm in length and is covered by connective tissue.
- At the center of the corpuscle is the inner bulb with fluid filled cavity having a single receptor ending without myelin and transmit pain.

Merkel nerve endings
- Merkel nerve endings are found in human skin and mucosa providing pressure and texture senses to the brain.
- The nerve ending consists of Merkel cell and enlarged nerve terminal. These are categorised as slow adapting mechanoreceptors.
- Free nerve ending is unspecialised nerve ending passing on skin pain senses to the human brain.
- Thermoreceptors are nerve endings in skin conveying the warm and cold perceptions to human brain.
- There are separate receptors for carrying the warm and cold senses.
- The warmth receptors are slower in transmitting the impulses when compared to cold receptors.
- Nociceptors are receptors that react and convey to human brain the senses of pain. These are specialised pain sensors.
-
Bulboid corpuscles are skin receptors which can detect low frequency of vibrations.
These are minute oval or cylindrical bodies consisting of soft core.
Hair follicle endings
- Hair follicle endings respond to displacement of hair and touch senses and are present in hairy areas of the human skin.
Topic of interest:
Causes of vitiligo skin disease.
Pityriasis alba white spots on children.
Olive oil moisturizer.
Baby milk spots.
White spots and patches on lips, fingernails, teeth, tonsils.
Homemade face moisturizer.
Hyperpigmentation pictures.
Albinism disorder causes.
What are the Causes of Hemangioma?
Cosmetic Laser Treatments.
Causes of vitiligo skin disease.
Pityriasis alba white spots on children.
Olive oil moisturizer.
Baby milk spots.
White spots and patches on lips, fingernails, teeth, tonsils.
Homemade face moisturizer.
Hyperpigmentation pictures.
Albinism disorder causes.
What are the Causes of Hemangioma?
Cosmetic Laser Treatments.
No comments:
Post a Comment