Skin care > Angioedema causes > Angioedema symptoms
The involvement of tongue or mucosa of the mouth or throat may cause stridor (a high-pitched wheezing sound) as the airway gets blocked progressively. In some cases anaphylaxis (anaphylactic shock) may occur characterized by a sharp drop in blood pressure. Both the situations require emergency medical care to prevent respiratory/cardiac arrest.
Appearance of symptoms of angioedema
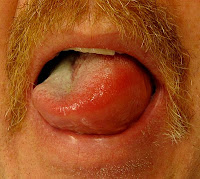
The swellings may appear over the period of minutes to hours. The swellings usually appear on the face, normally around the eyes and the mouth. The tongue may be affected partially or totally. In some cases, the swellings may affect the mucosa of the oral cavity and throat. The swelling can also appear elsewhere on the body, typically on the hands, feet or genitals.The affected parts of the body may show symptoms like itching or pain. Usually the affected parts of the body feel warm or hot and is of the same color as the surrounding unaffected area. However, in some conditions, the affected region may appear pink or red with inflammation. In some patients urticaria may also occur simultaneously. The edema in the genital parts can interfere with urination and require medical help.
In hereditary angioedema there may be recurrent episodes of abdominal pain followed by vomiting and diarrhea. There may be significant rise in the white blood cell count, which decreases when the symptoms diminish. These abdominal episodes may be very severe, requiring hospitalization for pain management. The symptoms like abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea are common to many abdominal ailments like appendicitis, gastric, duodenal and intestinal ulcers. Differential diagnosis and the study of the patient's history of earlier abdominal episodes may be able to pinpoint the cause of abdominal swellings and pain.
List of angioedema symptoms
- swelling below the skin
- presence of a firm swelling
- swelling of the face, hands, throat, feet or genitals
- painful sensation
- itchy sensation
- hot or warm sensation
- edema of the conjunctiva
- edema of the eyelids
- edema of the tongue
- edema of the oral cavity
- edema of the inside of the throat.
- severe chest tightness and pain
- stridor breathing
- difficulty in breathing
- trouble in swallowing
- symptoms of anaphylactic shock
- giddiness
- lightheadedness
- breathlessness
- rapid progression of swelling
- Abdominal pain or cramping
Related topics in dynamic nature skin care:
Angioedema definition.
Angioedema treatment.
Skin sensitive to touch.
List of skin diseases and disorders.
Makeup application tips.
Manuka honey for acne.
Honey mask for acne.
How to do natural look makeup.
Olive oil cleansing.
Hereditary angioedema.
Angioedema definition.
Angioedema treatment.
Skin sensitive to touch.
List of skin diseases and disorders.
Makeup application tips.
Manuka honey for acne.
Honey mask for acne.
How to do natural look makeup.
Olive oil cleansing.
Hereditary angioedema.
Popular topics in dynamic nature skin care:
Stratum lucidum function.
Stratum granulosum.
Epidermis parts.
Hives and angioedema.
Skin discoloration pictures.
Epidermis definition.
Epidermal keratinocytes.
Types of acne scars.
Homemade skin treatments.
Rhinophyma treatment.
Stratum lucidum function.
Stratum granulosum.
Epidermis parts.
Hives and angioedema.
Skin discoloration pictures.
Epidermis definition.
Epidermal keratinocytes.
Types of acne scars.
Homemade skin treatments.
Rhinophyma treatment.
Image source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Angioedema2013.JPG
Images author: James Heilman, MD
Images license: Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.
References:
1. Zuraw BL. Novel therapies for hereditary angioedema. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2006 Nov;26(4):691-708.
2. Angioedema | University of Maryland Medical Center http://umm.edu/health/medical/altmed/condition/angioedema
3..13.Levi M, Choi G, Picavet C, Hack CE. Self-administration of C1-inhibitor concentrate in patients with hereditary or acquired angioedema caused by C1-inhibitor deficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117:904.
Current topic: Angioedema swellings and symptoms
No comments:
Post a Comment