What is ingrown hair?
Ingrown hair occurs when the sharp, cut-end of thick hair grows sideways, at an abnormal angle, penetrating into the dermal skin.
Ingrown hair causes
- Shaving, tweezing or waxing are the primary causes of these ingrowths.
- Coarse or tightly curling thick hairs are the predisposing factors, as the cut end is more likely to bend back and grow into the skin leading to an inflammatory reaction.
- Individuals with higher levels of circulating androgenic hormones have excessive growth of thick hair and are prone to these ingrowths.
- Shaving very close to the skin can cut the hair strand deep inside the follicle and increase the risk of ingrowth.
- Shaving against the direction of growth causes the strands to get pulled and cut close to their root, increasing the risk of ingrowth.
- Friction from tight clothing, may precipitate the situation.
- Blocking of the follicle with dead skin debris may cause the strands to grow sideways.
- Certain genetic factors may predispose a person and cause these bumps in the beard area.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae, a type of extensive ingrowth, occurs in persons with thick, coarse hair. It is a common chronic inflammatory disorder in men of African ancestry, occurring most often in regions of thick hair growth after shaving. The condition causes erythematous papules with symptoms of pain and pus formation. A common polymorphism in a keratin gene (K6hf) may be a genetic risk factor for pseudofolliculitis barbae type of ingrowth.Ingrown hair symptoms
In most of the conditions, the symptoms may be limited to small reddish bumps. The symptoms like rash, tenderness and itching skin may also appear. Infected ingrowth may present symptoms such as pimple like inflammation, raised large bumps, abscesses and pruritic erythematous pustules. Certain other medical conditions like folliculitis, keratosis pilaris and furuncle may mimic the symptoms and are to differentially diagnosed.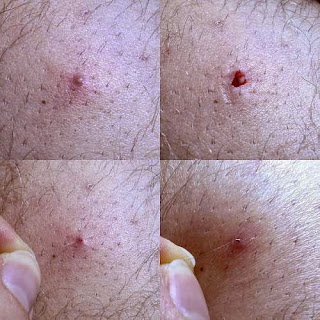 |
| Ingrown hair |
- inflammation,
- papules,
- pustules,
- hyperpigmentation,
- rash,
- pain,
- pruritus and
- embedded hairs in the site.
Ingrown hair treatment
Avoiding shaving for two to three weeks may causes the existing bumps to resolve. Extrafollicular ingrowths can usually be tweezed gently and cut above the skin level. Transfollicular ingrowths as well as ingrowths with symptoms of pus and severe inflammation may require medical treatment. Chemical depilatories, topical creams, laser therapy or surgical removal are the other treatment options available.Ingrown hair prevention
The best way to prevent the ingrowth is to refrain from shaving or using a beard trimmer. If shaving is necessary, wetting the skin with warm water and using a shaving gel may prevent the hair strand from getting pulled and getting cut close to the root. Avoiding shaving close to skin will enable the cut ends to grow out of the follicle smoothly. Shaving against the direction of the growth of strand must be avoided to prevent ingrown hair.Advertisements
|
References on ingrown hair: 1.Ribera M, Fernández-Chico N, Casals M. [Pseudofolliculitis barbae]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010 Nov;101(9):749-57. 2.Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014 Apr;32(2):183-91. |
Image author: LBPics | Image license: CC BY-SA 3.0
No comments:
Post a Comment