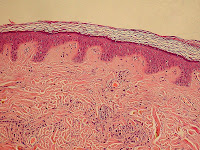
Skin hydration and skin desquamation are continuous processes in stratum corneum to keep it healthy.
Stratum corneum is the outermost layer of epidermis which in turn is the outermost part of skin.
Continuous hydration of the stratum corneum and continuous desquamation of dead skin cells is necessary to keep the skin soft, supple and smooth.
Any damage to these processes of hydration and desquamation results in scaly, rough and dry skin leading to many problems and diseases.
Skin hydration and stratum corneum
There is continuous production of cells at the lowermost layer of epidermis, basal layer.
The maturing cells move towards the outer most layer of epidemis (stratum corneum).
Here the cells die (now called corneocytes) and losing cellular structures and nuclei start the hydration and desquamation processes.
These corneocytes are flat and hexagonal in shape and are filled with keratin proteins ,which are hygroscopic in nature.
These keratin proteins are enveloped by lipids and proteins.
The shape of the corneocyte cells as well as structural orientation of the keratin proteins gives strength, hydration and pliability to stratum corneum.
Depending upon the area, 10-30 tiers of corneocyte layers can be found on the skin.
Desmosomes are protein bridges which connect the corneocytes, the loss which can cause desquamation.
Stacked Lipid layers surround the corneocyte extra cellular spaces.
The resultant stratum corneum structure of skin, functions as a natural physical and water-retaining cover helping skin hydration which is vital for desquamation.
Stratum corneum breakdown and skin hydration
Simultaneously during the movement of viable cells towards stratum corneum, proteins present in granular cell layer clump to form granules and get filled by filaggrin protein.
Keratin proteins form complexes with filaggrin proteins and resist proteolytic breakdown.
On reaching stratum corneum, enzymes breakdown filaggrin-keratin complex, for skin hydration and desquamation, with keratin remaining on the inside of the corneocytes and filaggrin occupying the outside.
When water content of the stratum corneum decreases, specific enzymes, proteolytic in nature, are released to breakdown filaggrin to its basic components, amino acids.
The amino acids along with salts, urea and lactic acid present in the stratum corneum, form natural factors of moisturizing, by attracting and holding water by their hygroscopic action.
Skin desquamation and stratum corneum
Apart from skin hydration, desquamation is an important process going on in the stratum corneum for the health and smoothness of skin.
Desquamation is again an enzymatic process in which the inter-cellular protein bridges of desmosomes are dissolved for shedding of the outer most layer of stratum corneum.
With the loss of protein bonds between them, cornecytes separate and their desquamation takes place.
These proteolytic enzymes, located in inter-cellular space, function well in presence of good hydration of stratum corneum.
In absence of hydration, these enzymes of desquamation do not function resulting in dry, thickened and scaly epidermis.
If the balance between the production of corneocytes and desquamation is upset, as in the case of many skin diseases and conditions, dry scaly skin is caused due accumulation of dead cells on its surface.
Intercellular lipids in skin hydration and desquamation of stratum corneum
The intercellular lipids are products of cell degradation of granular skin layer.
They surround the corneocytes and forming into stacks, they incorporate water into stratum corneum structure and accomplish its hydration.
The cell membranes also release lipids on degradation.
These lipids are mostly made up of sphingolipids (derived from the aliphatic amino alcohol sphingosine), fatty acids and cholesterol.
Ceramide is a major constituent of these lipids forming the stacked structure to trap molecules of water for epidermis hydration and desquamation.
These stacked lipids surround the corneocytes and form an impermeable barrier for moisture leaching out from the moisturizing factors formed naturally.
With old age inter-cellular lipids decrease sharply leading to reduced desquamation and dry scally epidermis conditions.
The water content of the outer epidermis (stratum corneum) fluctuates with environmental humidity.
There is a sharp TEWL (transepidermal water loss) in hot or cold dry air affecting the skin hydration and also desquamation of stratum corneum.